Your cart is currently empty!
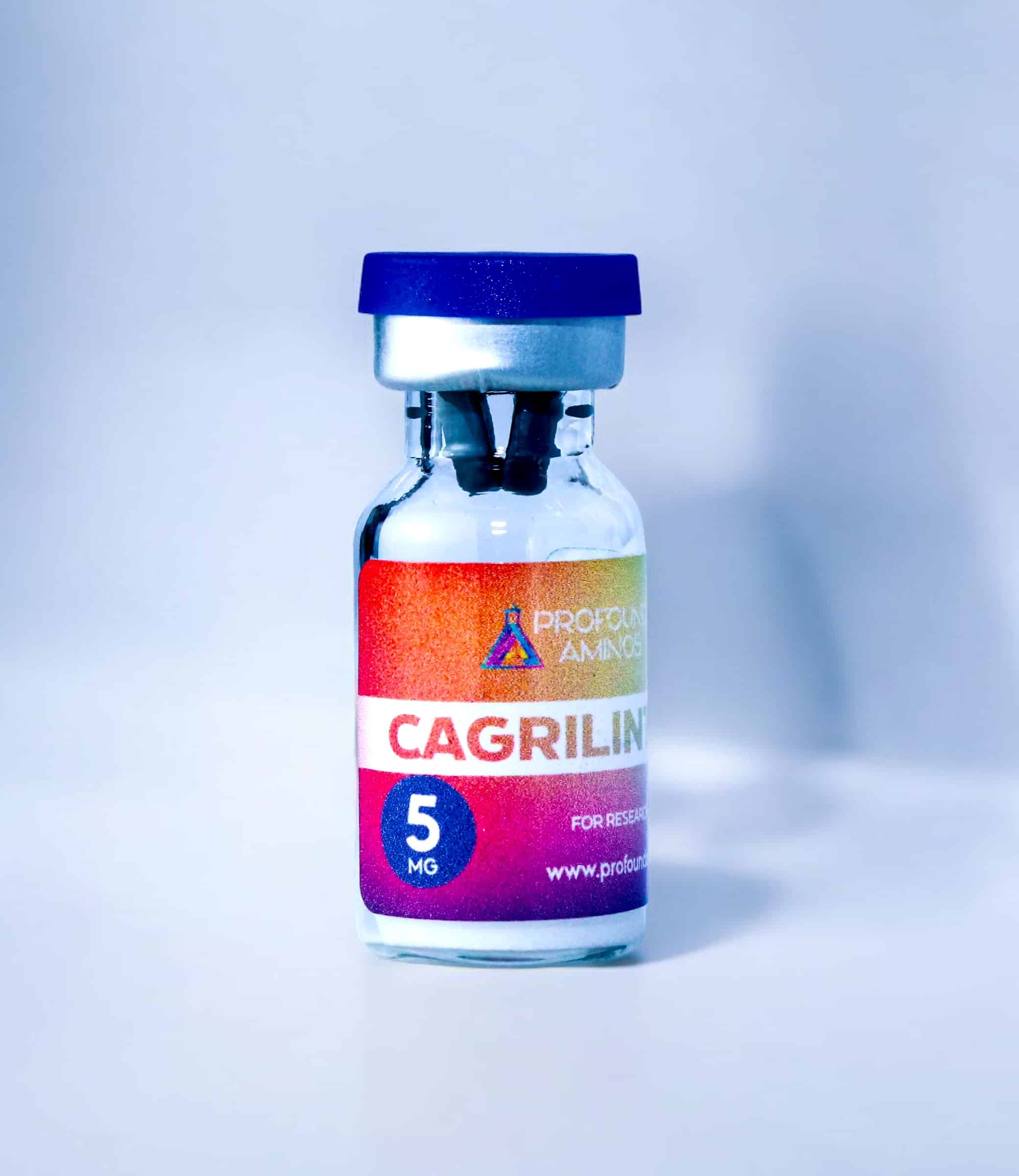
Cagri
Cagrilintide is a novel long-acting amylin analogue that has gained attention as a research compound for its potential role in appetite regulation, weight management, and metabolic health. As an analogue of the hormone amylin, cagrilintide is designed to enhance the natural effects of amylin in reducing food intake, promoting satiety, and regulating blood glucose. It […]
Description
Cagrilintide is a novel long-acting amylin analogue that has gained attention as a research compound for its potential role in appetite regulation, weight management, and metabolic health. As an analogue of the hormone amylin, cagrilintide is designed to enhance the natural effects of amylin in reducing food intake, promoting satiety, and regulating blood glucose. It is particularly interesting for research in obesity, metabolic disorders, and appetite control mechanisms.
Key Benefits of Cagrilintide for Research:
- Appetite Suppression and Satiety: Cagrilintide mimics the effects of amylin, a hormone co-secreted with insulin by the pancreas, to enhance feelings of fullness and reduce appetite. This makes it a valuable compound for research into appetite regulation, where understanding mechanisms of satiety and hunger are crucial, especially in studies related to obesity and eating disorders.
- Potential for Weight Management: Given its appetite-suppressing properties, cagrilintide is being researched for its potential in promoting weight loss. It helps reduce caloric intake by slowing gastric emptying and increasing the sensation of fullness. This makes it highly relevant for studies exploring pharmaceutical interventions for weight management and obesity treatment.
- Synergistic Effects with Other Weight-Loss Compounds: Cagrilintide has been investigated for its combined use with other metabolic compounds, such as GLP-1 receptor agonists like semaglutide, to enhance weight loss effects. Research exploring combination therapies that target different aspects of appetite regulation and metabolism stands to benefit from cagrilintide’s unique profile.
- Glucose Regulation and Metabolic Health: Amylin plays a role in glucose regulation by slowing the rate at which food moves from the stomach to the small intestine, which in turn affects the speed of glucose absorption into the bloodstream. Cagrilintide, as an amylin analogue, could be important in studies focused on glucose homeostasis, insulin sensitivity, and overall metabolic health, making it relevant for diabetes research.
- Potential for Treatment of Metabolic Disorders: Beyond weight loss, cagrilintide is of interest in broader research on metabolic syndromes and related conditions, such as insulin resistance and dyslipidemia. By influencing both energy intake and glucose metabolism, it provides a promising approach for studying interventions for metabolic health improvement.
- Long-Acting Action: Cagrilintide’s long-acting profile allows for more sustained effects on satiety and metabolic regulation compared to natural amylin, making it a key tool in research designs requiring long-term studies of appetite control and weight management interventions.
Additional information
| Strength | 5mg |
|---|