Your cart is currently empty!
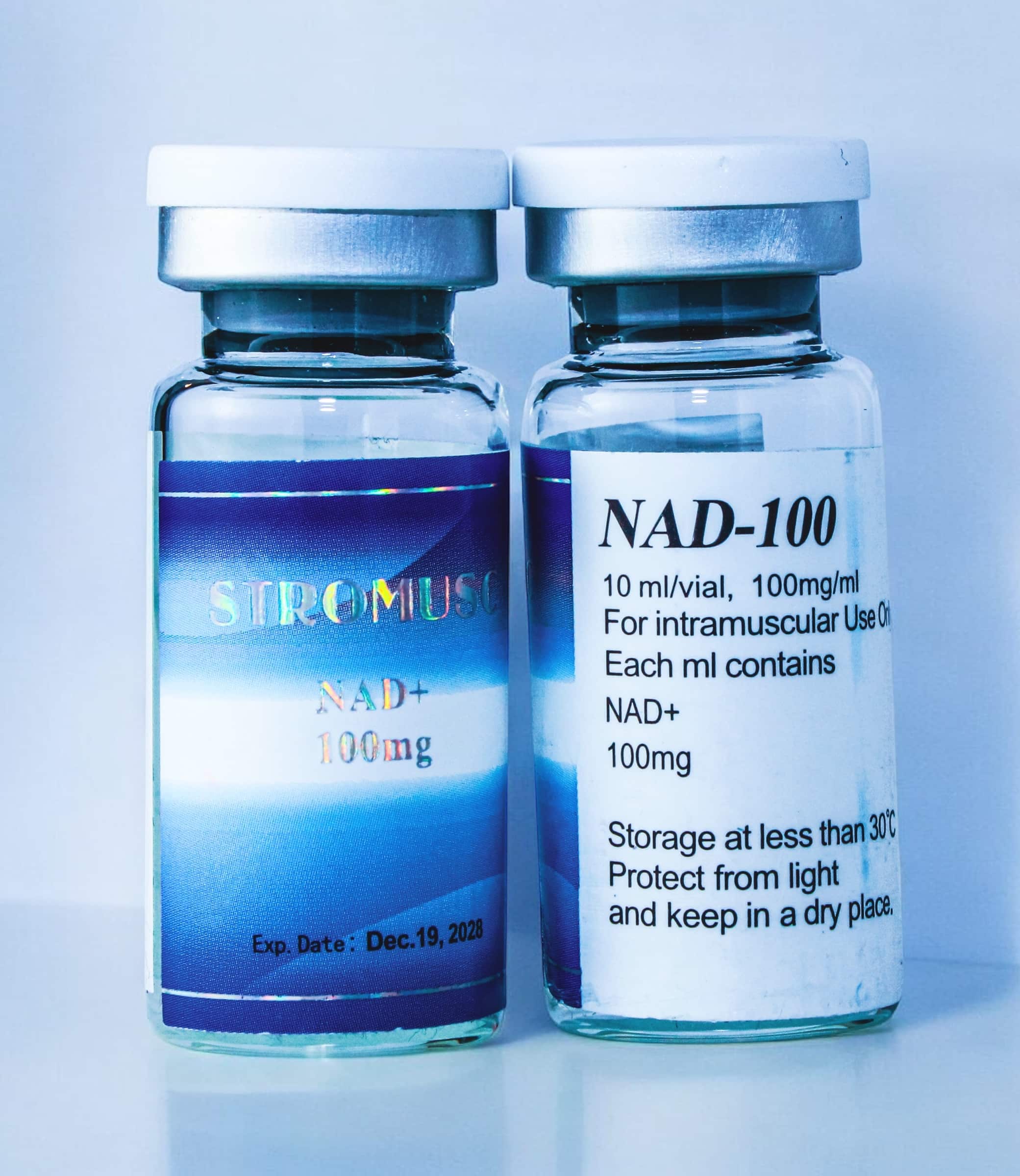
NAD+ 1000mg
1000mg vial 100mg/ml x 10ml NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide): NAD+ is a coenzyme that plays a central role in cellular energy metabolism and is essential for various biochemical processes, including DNA repair, gene expression, and mitochondrial function. As a vital molecule involved in redox reactions, NAD+ facilitates the transfer of electrons between molecules, enabling cells […]
In stock
Description
1000mg vial 100mg/ml x 10ml
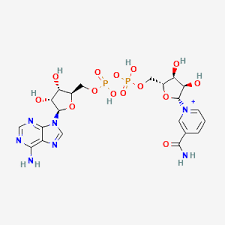
NAD+ (Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide):
NAD+ is a coenzyme that plays a central role in cellular energy metabolism and is essential for various biochemical processes, including DNA repair, gene expression, and mitochondrial function. As a vital molecule involved in redox reactions, NAD+ facilitates the transfer of electrons between molecules, enabling cells to generate ATP (adenosine triphosphate), the primary energy source for cellular activities. NAD+ has garnered significant attention in research for its potential applications in aging, neurodegenerative diseases, metabolic health, and overall cellular function.
Key Benefits of NAD+ for Research:
- Role in Energy Metabolism: NAD+ is a key player in the conversion of nutrients into cellular energy. It functions as a critical cofactor for enzymes involved in glycolysis, the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle, and oxidative phosphorylation, all of which are central to ATP production. Researchers exploring mitochondrial health, cellular energy metabolism, and metabolic disorders like diabetes and obesity use NAD+ to investigate how cellular energy balance is regulated and how energy deficits can contribute to disease.
- DNA Repair and Genomic Stability: NAD+ is essential for the activity of sirtuins and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerases (PARPs), both of which are enzymes involved in DNA repair and the maintenance of genomic stability. Sirtuins, in particular, are implicated in regulating cellular longevity and stress resistance. Studies focused on aging, cancer, and cellular senescence can benefit from NAD+ as it is crucial for maintaining healthy DNA and mitigating damage caused by environmental and oxidative stressors.
- Neuroprotection and Cognitive Health: NAD+ is critical for maintaining neuronal function and has been studied for its neuroprotective properties. The compound has the potential to enhance brain health by supporting mitochondrial function, reducing oxidative stress, and promoting the repair of damaged neurons. As such, NAD+ is a valuable tool in research exploring neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, and Huntington’s diseases, as well as cognitive decline and memory disorders.
- Anti-Aging and Longevity: NAD+ levels naturally decline with age, and this depletion is associated with reduced mitochondrial function, increased oxidative stress, and diminished cellular repair mechanisms. Research into NAD+ supplementation or boosting NAD+ levels has shown promise in delaying or even reversing certain aspects of aging. It plays a key role in studies on longevity, age-related decline in organ function, and interventions aimed at slowing the aging process.
- Sirtuin Activation and Cellular Health: Sirtuins are a family of proteins that regulate several important cellular processes, including aging, inflammation, and stress resistance, and they require NAD+ for their activation. By boosting NAD+ levels, researchers can study how sirtuins influence cellular health, lifespan, and resistance to age-related diseases. This makes NAD+ a critical compound for exploring therapeutic strategies targeting metabolic and inflammatory pathways.
- Metabolic Health and Insulin Sensitivity: NAD+ is integral to maintaining metabolic homeostasis and insulin sensitivity. It regulates pathways involved in glucose and lipid metabolism, making it relevant for research into type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and obesity. Studies investigating the relationship between NAD+ levels and metabolic dysfunction are important for understanding how energy imbalances can lead to chronic diseases.
- Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Function: NAD+ is essential for mitochondrial function and biogenesis, as it supports the production of ATP and promotes the removal of dysfunctional mitochondria via mitophagy. This is particularly important in the context of aging, as mitochondrial decline is a hallmark of many age-related diseases. Research using NAD+ helps elucidate how mitochondrial health impacts overall cellular function and how boosting NAD+ levels can improve mitochondrial efficiency.
Why Use NAD+ in Research?
- Central to Cellular Energy Production: NAD+ is indispensable for cellular respiration and energy metabolism, making it a crucial component in studies related to mitochondrial health, metabolic disorders, and ATP production.
- DNA Repair and Longevity: As a cofactor for enzymes involved in DNA repair and sirtuin activation, NAD+ is central to research on aging, genomic stability, and cellular repair mechanisms.
- Neuroprotection and Cognitive Function: NAD+ has shown promise in neuroprotection, making it highly relevant for research into neurodegenerative diseases, cognitive health, and brain aging.
- Potential Anti-Aging Interventions: NAD+ supplementation and its role in sirtuin activation make it a promising candidate for studies on longevity and age-related diseases.
- Broad Metabolic Applications: NAD+ is critical for insulin sensitivity and metabolic regulation, supporting its use in research on diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome.
NAD+ is a vital research compound that plays a key role in a broad spectrum of biological processes, including energy metabolism, DNA repair, neuroprotection, and aging. Its potential applications in metabolic health, neurodegeneration, and longevity make NAD+ an invaluable tool for advancing research in cellular function and disease prevention.
Structure: