Your cart is currently empty!
Reta
Retatrutide – The New Peptide Darling Retatrutide is an investigational, multi-receptor agonist designed to target the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), and glucagon receptors. This novel mechanism of action allows it to simultaneously influence multiple metabolic pathways, making it an exciting compound for research into obesity, type 2 diabetes, and related metabolic disorders. […]
In stock
Description
Retatrutide – The New Peptide Darling
Retatrutide is an investigational, multi-receptor agonist designed to target the glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), and glucagon receptors. This novel mechanism of action allows it to simultaneously influence multiple metabolic pathways, making it an exciting compound for research into obesity, type 2 diabetes, and related metabolic disorders. By combining the effects of these three receptor pathways, retatrutide offers a promising approach to treating complex metabolic conditions through improved weight management, glycemic control, and lipid metabolism.
Key Benefits of Retatrutide for Research:
- Multi-Receptor Agonism: Retatrutide’s unique ability to activate GLP-1, GIP, and glucagon receptors provides a comprehensive approach to metabolic regulation. GLP-1 agonism promotes insulin secretion and appetite suppression, GIP enhances insulin response and fat metabolism, and glucagon stimulates energy expenditure and lipid breakdown. This multi-receptor engagement makes retatrutide an attractive compound for studying the combined effects of these pathways in metabolic health.
- Significant Weight Loss Potential: One of retatrutide’s most notable effects is its ability to promote substantial weight loss. By reducing appetite and increasing energy expenditure through its action on the GLP-1 and glucagon receptors, retatrutide has shown promise as a powerful weight-loss agent. Researchers focused on obesity and weight management can use retatrutide to explore the mechanisms behind pharmacologically-induced weight loss and its long-term effects on body composition.
- Glycemic Control: Retatrutide’s action on the GLP-1 and GIP receptors enhances insulin secretion in response to glucose, leading to better glycemic control and lower blood glucose levels. This makes it a key compound for research into type 2 diabetes management, as it may provide more comprehensive glucose regulation compared to single-receptor agonists. Its ability to improve insulin sensitivity while reducing hyperglycemia makes it ideal for studying metabolic disorders.
- Improved Lipid Metabolism: By activating the glucagon receptor, retatrutide stimulates the breakdown of stored fat (lipolysis) and increases energy expenditure. This effect on lipid metabolism makes retatrutide an exciting compound for research into conditions like dyslipidemia, metabolic syndrome, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Researchers can investigate how this compound influences fat metabolism, weight loss, and lipid profiles in both obese and non-obese populations.
- Potential Cardiovascular Benefits: Retatrutide’s impact on glycemic control, weight loss, and lipid metabolism may also lead to cardiovascular benefits, such as improved cholesterol levels, reduced blood pressure, and decreased cardiovascular risk. Given the strong association between metabolic disorders and cardiovascular disease, retatrutide is relevant for research focused on heart health, particularly in patients with obesity and diabetes.
- Enhanced Energy Expenditure: The glucagon receptor agonism component of retatrutide increases energy expenditure, which is critical for addressing obesity and metabolic disorders. By promoting fat burning and enhancing caloric output, retatrutide offers researchers a compound that affects both sides of the energy balance equation, making it valuable for studying long-term weight loss and maintenance.
- Potential for Combination Therapies: Retatrutide’s ability to engage multiple metabolic pathways simultaneously opens the door for research into combination therapies, where it may be paired with other compounds to enhance therapeutic outcomes. This flexibility in treatment design makes it a useful tool in the development of more effective interventions for diabetes, obesity, and metabolic syndrome.
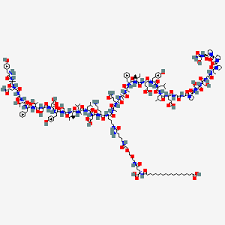
Retatrutide Structure:
Additional information
| Strength | 10mg |
|---|